lv constant | 11.3 Phase Change and Latent Heat lv constant Learn how latent heat of fusion (Lf) and latent heat of vaporisation (Lv) are defined and calculated for different materials. See examples of problems involving changes of state and energy transfers. Media related to Air Malta at Wikimedia Commons• Official website See more
0 · Left ventricular mass and volume (size) – Cardiovascular Education
1 · Energy Matters – Heat Changes of State
2 · 14.3 Phase Change and Latent Heat
3 · 11.3 Phase Change and Latent Heat
For vintage reading glasses, sunglasses, and prescription-ready eye glass frames for men and women, buy designer glasses online through AJ Morgan Eyewear.Whether you’re looking for a timeless style or something fun and unique, we offer a selection of original and vintage-inspired sunglasses to suit your every mood. Choose .
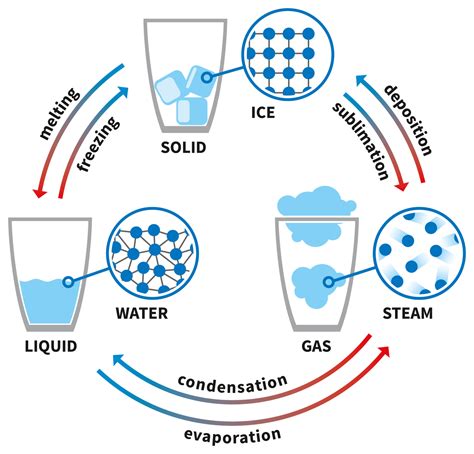
Learn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Find out how latent heat depends on the type and strength of molecular forces and how to calculate final temperature from heat transfer.
 – Cardiovascular Education.jpg)
Learn how latent heat of fusion (Lf) and latent heat of vaporisation (Lv) are defined and .Learn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, .
Learn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Find out how latent heat depends on the type and strength of molecular forces and how to calculate final temperature from heat transfer.
Learn how latent heat of fusion (Lf) and latent heat of vaporisation (Lv) are defined and calculated for different materials. See examples of problems involving changes of state and energy transfers.Learn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, freezing, boiling, and condensation. Find out the specific latent heat of fusion and vaporization for different substances and how to solve problems involving thermal energy changes.Learn about the latent heat of fusion and vaporization, the energy required or released during phase changes of substances. Find out how to calculate the heat involved in melting, freezing, evaporating, and condensing.
Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction induces the increase of LV diastolic pressure and subsequently of left atrial and pulmonary capillary pressures independent of systolic function, resulting in the onset of heart failure.Learn how to calculate and interpret left ventricular mass and volume using echocardiography. Find out the formulas, normal values, and criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy. Left ventricular diastolic time constant is suggested because left ventricular diastolic process is an active process. Left ventricular systolic process is also an active process, so are right ventricular diastolic and systolic processes.
From this logistic model, we successfully derived a new “logistic” time constant (T L) that is superior to the conventional “exponential” time constant (T E) for evaluating LV lusitropism.Default assumptions are ‘ideal gas’, ‘hydrostatic’, ‘constant g’, ‘constant Lv’, ‘constant Cp’, ‘no liquid water’, ‘no ice’, ‘bolton’, ‘cimo’. Assumption descriptions. bolton – the assumptions in Bolton (1980) hold; cimo – the CIMO guide equation for esi; constant Cp – .The LabVIEW Object is the common ancestor data type for all LabVIEW classes. You can use the LabVIEW Object Constant to create generic methods that can handle all LabVIEW class data types. UsageLearn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation. Find out how latent heat depends on the type and strength of molecular forces and how to calculate final temperature from heat transfer.
Learn how latent heat of fusion (Lf) and latent heat of vaporisation (Lv) are defined and calculated for different materials. See examples of problems involving changes of state and energy transfers.Learn how latent heat is the energy involved in phase changes of matter, such as melting, freezing, boiling, and condensation. Find out the specific latent heat of fusion and vaporization for different substances and how to solve problems involving thermal energy changes.
Left ventricular mass and volume (size) – Cardiovascular Education
Learn about the latent heat of fusion and vaporization, the energy required or released during phase changes of substances. Find out how to calculate the heat involved in melting, freezing, evaporating, and condensing. Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction induces the increase of LV diastolic pressure and subsequently of left atrial and pulmonary capillary pressures independent of systolic function, resulting in the onset of heart failure.Learn how to calculate and interpret left ventricular mass and volume using echocardiography. Find out the formulas, normal values, and criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy. Left ventricular diastolic time constant is suggested because left ventricular diastolic process is an active process. Left ventricular systolic process is also an active process, so are right ventricular diastolic and systolic processes.
rolex yacht-master 37mm review
From this logistic model, we successfully derived a new “logistic” time constant (T L) that is superior to the conventional “exponential” time constant (T E) for evaluating LV lusitropism.Default assumptions are ‘ideal gas’, ‘hydrostatic’, ‘constant g’, ‘constant Lv’, ‘constant Cp’, ‘no liquid water’, ‘no ice’, ‘bolton’, ‘cimo’. Assumption descriptions. bolton – the assumptions in Bolton (1980) hold; cimo – the CIMO guide equation for esi; constant Cp – .
rolex.yatch master
Energy Matters – Heat Changes of State
14.3 Phase Change and Latent Heat

25 Overseas Aircraft Mechanic jobs available on Indeed.com. Apply to Aircraft Mechanic, Aircraft Mechanic II, Aviation Manager and more!
lv constant|11.3 Phase Change and Latent Heat



























